Sleep Apnea: Symptoms, Risks & Life-Changing Treatments

Sleep apnea is a serious medical condition where breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep. The most common form, Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA), occurs when throat muscles relax and block the airway. Key symptoms include loud snoring, episodes of gasping or choking during sleep, and excessive daytime sleepiness. If left untreated, sleep apnea significantly increases the risk for major health problems like high blood pressure, heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. Fortunately, highly effective treatments, primarily Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy, can manage the condition, restore sleep quality, and reduce these health risks.
This guide provides a detailed overview of sleep apnea, from recognizing its subtle signs to understanding the proven treatments that can dramatically improve health and daily life. The information is based on established clinical knowledge and is designed to give you a clear picture of this common but often undiagnosed disorder.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Sleep Apnea
The signs of sleep apnea are not always obvious and can be easily mistaken for simple fatigue or stress. While loud, chronic snoring is a hallmark symptom, many other indicators can point to a problem.
Nighttime Symptoms:
- Loud, persistent snoring
- Observed pauses in breathing by a bed partner
- Abrupt awakenings accompanied by gasping or a choking sensation
- Waking up frequently to urinate (nocturia)
- Restless sleep and night sweats
Daytime Symptoms:
- Excessive daytime sleepiness (feeling tired despite a full night’s sleep)
- Waking up with a dry mouth or a sore throat
- Morning headaches
- Difficulty concentrating or memory problems
- Irritability and mood changes
Bonus Tip: Since many symptoms occur during sleep, a bed partner’s observations are incredibly valuable. Ask them if they’ve noticed you snoring loudly, stopping breathing, or making choking sounds. This information is very helpful for a physician.
The Health Risks of Untreated Sleep Apnea
The repeated breathing pauses caused by sleep apnea lead to drops in blood oxygen levels. This puts immense strain on the cardiovascular system and can lead to severe long-term health consequences. A study published by the American Heart Association found a strong link between obstructive sleep apnea and an increased risk of hypertension and cardiovascular events.
When breathing stops, the brain briefly wakes you up to restart it. These micro-awakenings can happen hundreds of times a night, preventing you from reaching the deep, restorative stages of sleep. The long-term effects of this cycle include:
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): The sudden drops in oxygen trigger a stress response in the body, which can raise blood pressure over time.
- Heart Problems: The strain on the heart increases the risk of heart attacks, heart failure, and irregular heartbeats (atrial fibrillation).
- Stroke: Research from the National Institutes of Health indicates that sleep apnea is a significant independent risk factor for stroke.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Sleep apnea can contribute to insulin resistance, a precursor to diabetes.
- Daytime Impairment: Chronic fatigue impairs cognitive function, increasing the risk of workplace accidents and car crashes.
Life-Changing Treatment Options
Once diagnosed through a sleep study, sleep apnea is a very manageable condition. The goal of treatment is to keep the airway open during sleep, which eliminates breathing pauses and allows for uninterrupted, restorative rest.
Comparing Common Sleep Apnea Treatments
| Treatment Method | How It Works | Best For | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| CPAP Therapy | A machine delivers a steady stream of pressurized air through a mask to keep the airway open. | Mild, moderate, and severe OSA. | The most effective treatment available. Requires consistent nightly use. Mask comfort is key. |
| Oral Appliances | A custom-fit, mouthguard-like device repositions the jaw or tongue to prevent airway collapse. | Mild to moderate OSA; patients who cannot tolerate CPAP. | Must be fitted by a qualified dentist. Less effective for severe cases. |
| Positional Therapy | Devices that prevent you from sleeping on your back, where airway collapse is more likely. | Mild OSA occurs primarily when sleeping on the back. | Often used in combination with other therapies. Not a standalone solution for most people. |
- Bonus Tip: Finding the right CPAP mask is the most important factor for success. There are many styles available (nasal pillows, nasal masks, full-face masks). Don’t be discouraged if the first one you try isn’t a perfect fit. Working with your equipment provider to try different options is standard practice.
- Regional Guidance: In areas like New York, seasonal allergies can cause nasal congestion that makes CPAP use more challenging. Using a CPAP machine with a heated humidifier and saline nasal sprays can help manage congestion and improve comfort.
Things to Consider Before Seeking a Diagnosis
If you suspect you have sleep apnea, a few preparatory steps can make the diagnostic process more effective.
- Track Your Symptoms: Keep a simple log of your daytime sleepiness levels, any headaches, and feedback from your bed partner. Note how many hours you sleep versus how rested you feel.
- Review Your Medical History: Be ready to discuss any related conditions you have, such as hypertension, heart disease, or diabetes, as well as any family history of sleep apnea.
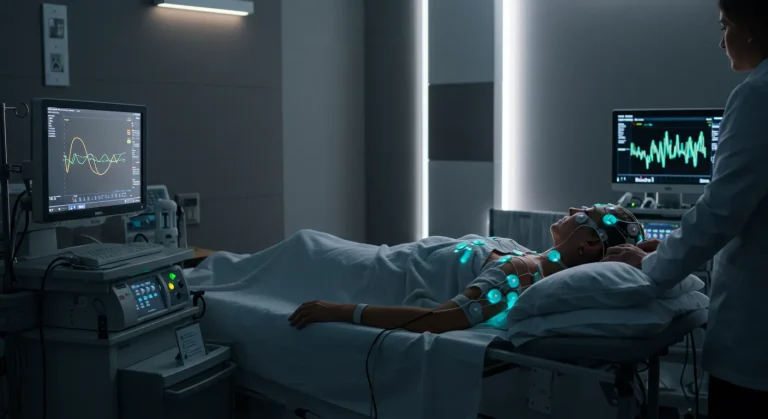
- Prepare for a Sleep Study: The definitive diagnosis for sleep apnea is made with a sleep study. Understand that this is a non-invasive test designed to get a clear picture of your sleep patterns.
Common Questions About Sleep Apnea
Can sleep apnea be cured by losing weight?
Weight loss can significantly reduce the severity of sleep apnea for many people, and in some cases of mild OSA, it can resolve the issue. However, it is not a guaranteed cure, as many people at a healthy weight also have sleep apnea due to their anatomy.
Is surgery a good option?
Surgical options exist but are typically reserved for specific cases where there is a clear anatomical obstruction (like enlarged tonsils). They are generally considered only after other treatments have been unsuccessful.
What is the difference between obstructive and central sleep apnea?
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) is a mechanical problem where the airway is blocked. Central Sleep Apnea (CSA) is a neurological issue where the brain fails to send the proper signals to the muscles that control breathing. OSA is far more common.
Answering Your Questions About Treatment
Will I have to use a CPAP machine forever?
For most people, sleep apnea is a chronic condition, and CPAP is a long-term therapy. Think of it like managing high blood pressure with medication. Consistent use is necessary to prevent symptoms and health risks from returning.
Are modern CPAP machines loud?
No. Today’s CPAP machines are whisper-quiet and very compact. Most background noise, like a fan or air conditioner, is louder than the machine itself.
How do I clean my CPAP equipment?
Daily cleaning of the mask cushion and weekly cleaning of the tubing and water chamber with mild soap and water is recommended. Regular maintenance is simple and prevents the buildup of germs.
What happens if I miss a night of therapy?
Missing one night is not a major issue, but you will likely notice your symptoms, like snoring and daytime fatigue, return immediately. The long-term health benefits depend on consistent use.
The Path to Better Sleep and Health
Ignoring the signs of sleep apnea means accepting a lower quality of life and exposing yourself to serious health dangers. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the risks is the first step. A proper diagnosis through a sleep study provides the clarity needed to begin treatment. With today’s effective therapies, managing sleep apnea can lead to a profound improvement in energy, mental clarity, and overall health.
Getting a Definitive Answer
If the symptoms described here sound familiar, the next step is a professional evaluation. A formal sleep study is the only way to accurately diagnose sleep apnea and determine its severity. To understand the diagnostic process at Vector Sleep Diagnostic Center, you can inquire via email at vectorsleep@gmail.com or by calling (718) 830-2800. A clear diagnosis is the starting point for reclaiming your health and getting a truly restful night’s sleep.





