Insomnia: Understanding the Risks and Solutions
Are you tired of tossing and turning at night, unable to get a restful night’s sleep? Look no further than Vector Sleep Clinic, conveniently located in the heart of Rego Park and easily accessible from all 5 boroughs. We understand the risks and impact of sleep disorders like insomnia, sleep apnea, and more, and we’re here to help. If left untreated, these disorders can lead to serious health issues such as heart attacks, strokes, high blood pressure, and even car accidents. But don’t worry, our licensed and insured clinic offers comprehensive care for restful sleep. Say goodbye to sleepless nights and unlock the magic of rejuvenation at Vector Sleep Clinic.
This image is property of my.clevelandclinic.org.
Understanding Insomnia
Insomnia is a common sleep disorder characterized by difficulties in falling asleep, staying asleep, waking up too early, and not feeling rested after a night’s sleep. It is important to understand the definition and symptoms of insomnia in order to effectively recognize and address this issue.
Definition and Symptoms
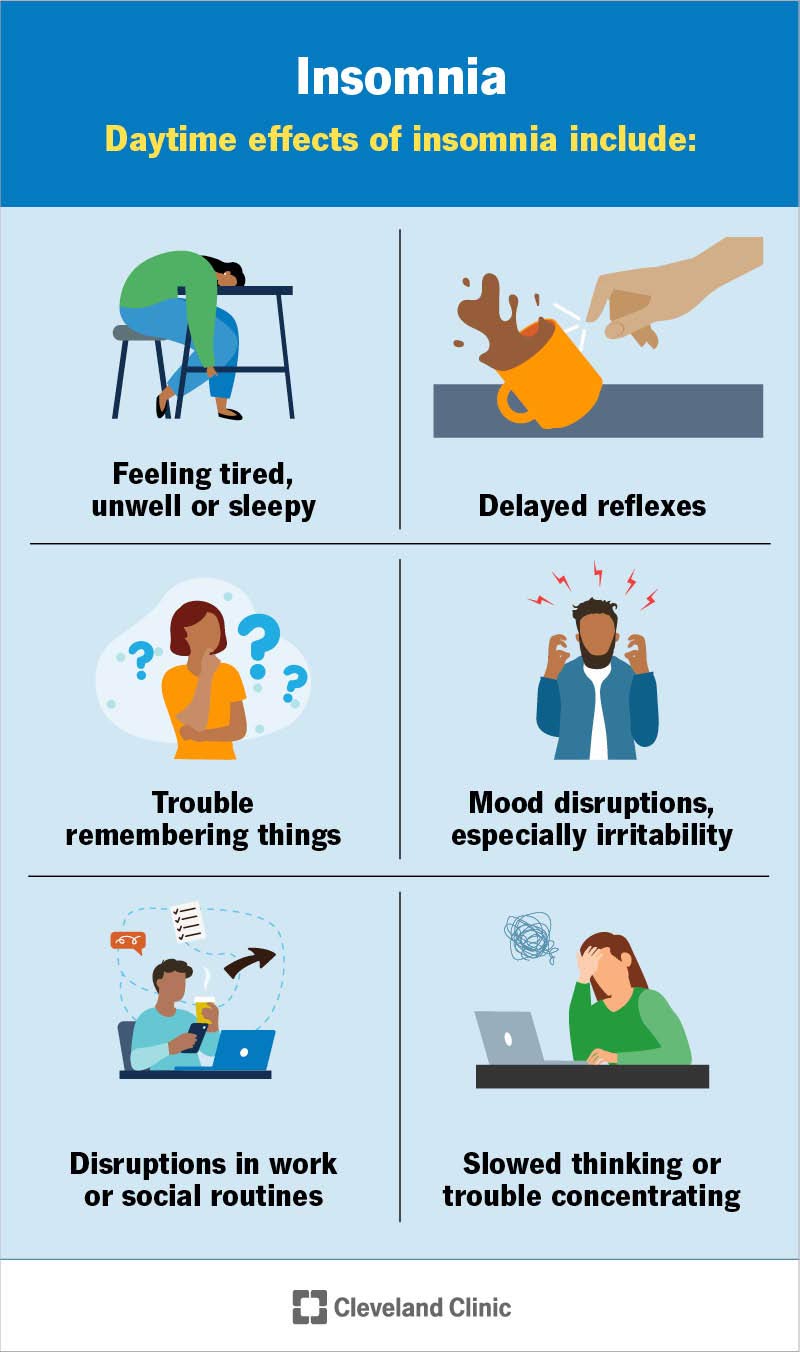
Insomnia is defined as a persistent difficulty in initiating or maintaining sleep. It is often accompanied by daytime symptoms such as fatigue, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and impaired performance. Individuals with insomnia may experience a range of symptoms, including a racing mind, excessive worrying, physical discomfort, and a general sense of restlessness.
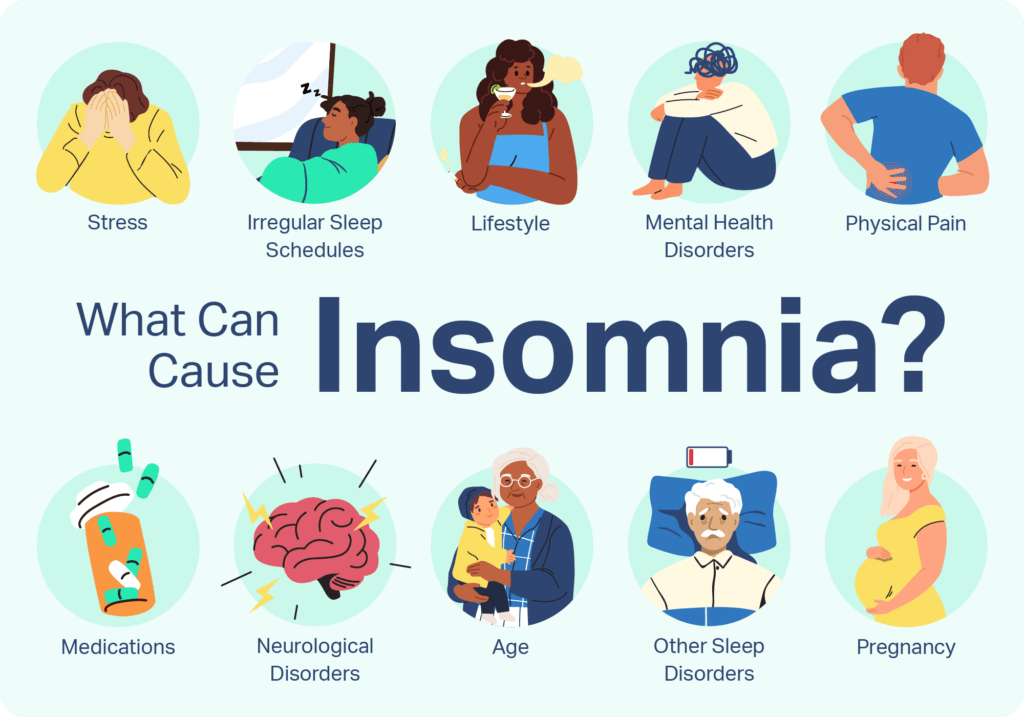
Causes of Insomnia
Insomnia can have various causes, both psychological and physical. Stress, anxiety, depression, and other mental health conditions can contribute to the development of insomnia. Additionally, certain medical conditions, such as chronic pain, sleep apnea, and Restless leg syndrome, can disrupt sleep patterns and lead to insomnia. External factors, such as poor sleep habits, excessive caffeine or alcohol intake, and exposure to blue light from screens, can also contribute to the development of insomnia.
Types of Insomnia
There are two main types of insomnia: primary insomnia and secondary insomnia. Primary insomnia refers to insomnia that is not directly associated with any other medical or psychiatric condition. Secondary insomnia, on the other hand, is insomnia that occurs as a symptom of another underlying condition, such as depression or sleep apnea.
Insomnia as a Symptom of Other Conditions
In some cases, insomnia may be a symptom of other medical or psychiatric conditions. This means that addressing and treating the underlying condition is crucial in managing insomnia. Conditions such as sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, mental health disorders, and chronic pain can all manifest as insomnia symptoms. Identifying and treating these underlying conditions can help alleviate insomnia and improve overall sleep quality.
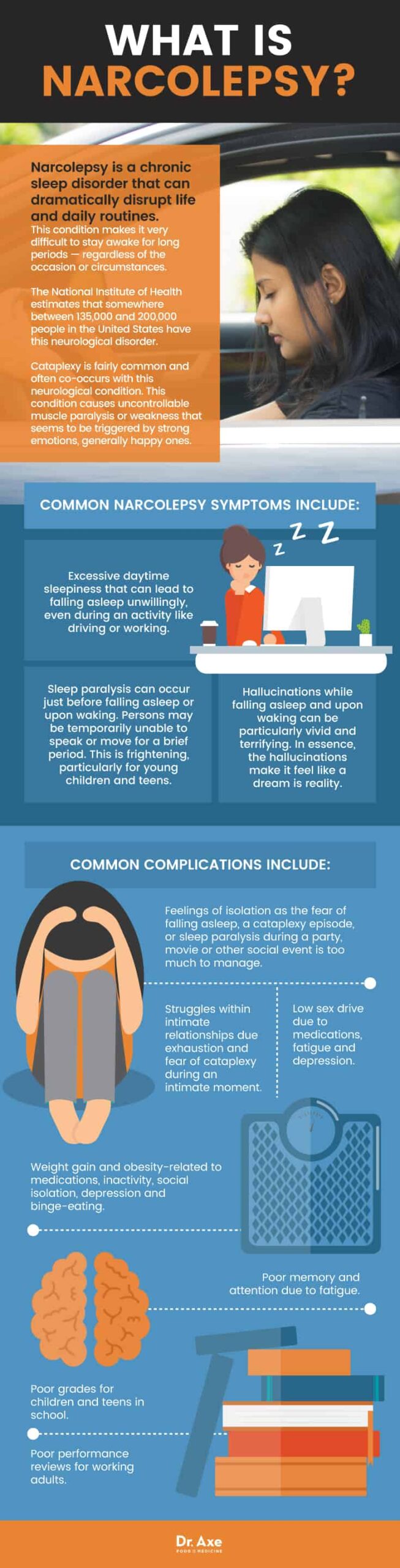
The Impact of Insomnia on Health
Insomnia can have a significant impact on both physical and mental health. Understanding the potential health risks and complications associated with insomnia is key to recognizing the importance of addressing this sleep disorder.
Physical Health Risks
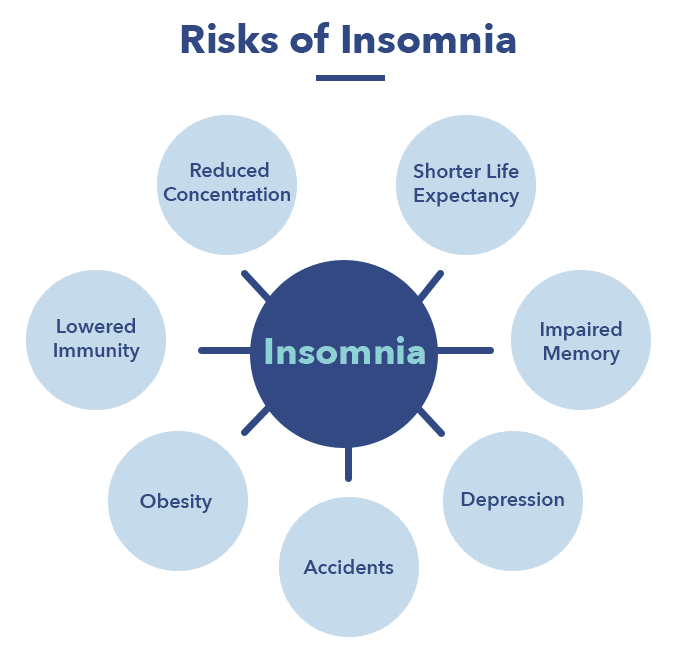
Chronic insomnia has been linked to a number of physical health risks. These risks include an increased likelihood of developing conditions such as obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and hypertension. Insufficient sleep can also weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections and illnesses. Additionally, insomnia has been associated with an increased risk of accidents and injuries due to decreased alertness and impaired cognitive function.
Mental Health Complications
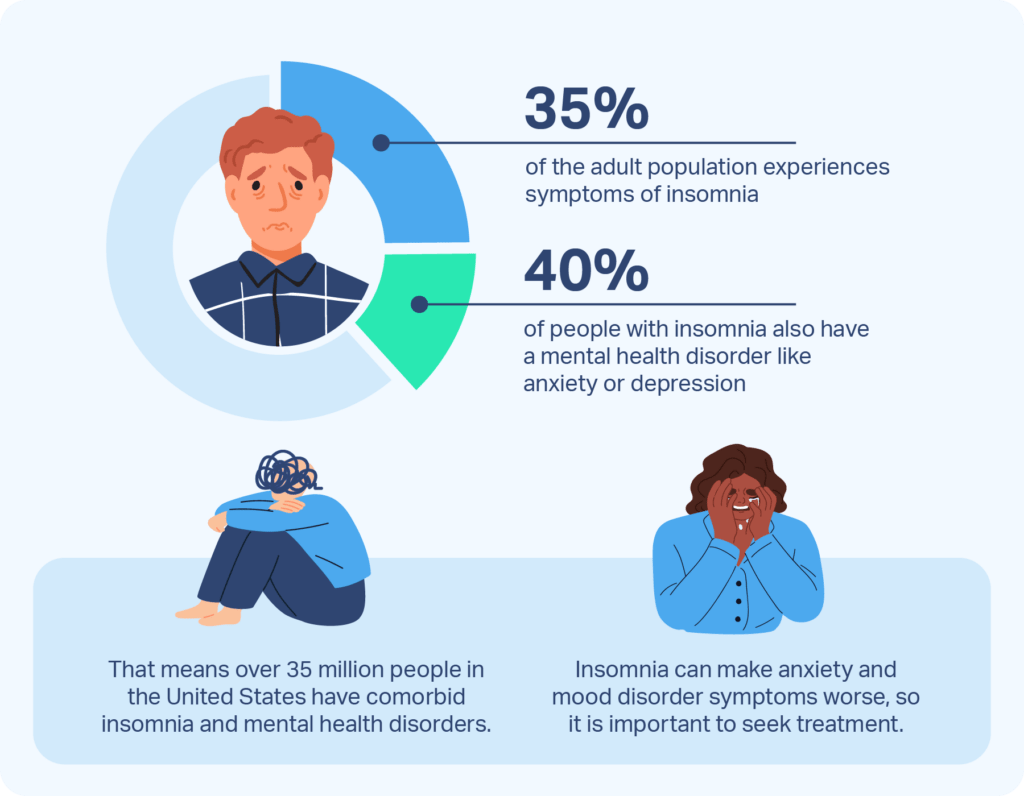
Insomnia is closely linked to mental health complications. It can exacerbate existing mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression, and can even contribute to the development of these conditions. Lack of sleep can negatively impact mood regulation, cognitive function, and overall emotional well-being. The relationship between insomnia and mental health is complex, and addressing insomnia is an essential component of managing mental health concerns.
Long-Term Consequences
If left untreated, insomnia can have long-term consequences on overall health and well-being. Chronic insomnia can lead to persistent fatigue, decreased productivity, and difficulty concentrating. It can also negatively impact relationships, work performance, and quality of life. Addressing insomnia early on is crucial in preventing the potential long-term consequences associated with this sleep disorder.
Recognizing the Signs of Insomnia
Recognizing the signs of insomnia is an important step in seeking appropriate treatment. Being able to identify the common symptoms of insomnia can help individuals understand their sleep patterns and seek the necessary help.
Difficulties in Falling Asleep
One of the primary signs of insomnia is difficulty falling asleep. Individuals may find themselves lying awake in bed for extended periods of time, unable to transition into sleep despite feeling tired. This can be frustrating and can create a cycle of anxiety and anticipation around bedtime.
Trouble Staying Asleep
Another common symptom of insomnia is trouble staying asleep throughout the night. Individuals may find themselves waking up multiple times during the night and struggling to fall back asleep. This can result in fragmented sleep and a feeling of unrestfulness in the morning.
Waking Up Too Early
Some individuals with insomnia may experience early morning awakenings, where they wake up significantly earlier than intended and are unable to fall back asleep. This can lead to a sense of fatigue and grogginess throughout the day.
Not Feeling Rested After a Night’s Sleep
A key indicator of insomnia is not feeling rested after a night’s sleep. Despite spending the recommended amount of time in bed, individuals with insomnia may wake up feeling tired and unrefreshed. This can contribute to daytime sleepiness and impair cognitive function.
Insomnia and Lifestyle
Several lifestyle factors can impact the development and severity of insomnia. Understanding the relationship between lifestyle choices and insomnia is essential in managing this sleep disorder effectively.
The Role of Stress
Stress is a significant contributor to insomnia. When individuals experience high levels of stress, their bodies may enter a state of hyperarousal, making it difficult to relax and fall asleep. Managing stress through techniques such as meditation, relaxation exercises, and therapy can help alleviate insomnia symptoms.
Diet and Exercise
Diet and exercise play a crucial role in sleep quality. Consuming a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods can promote better sleep. Regular exercise can also improve sleep quality by reducing anxiety, promoting relaxation, and regulating sleep-wake cycles. It is important to establish healthy eating and exercise routines for better sleep.
Screen Time and Blue Light Exposure
Excessive screen time and exposure to blue light can disrupt the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle. The blue light emitted by electronic devices can suppress the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep. Limiting screen time, especially before bed, and using blue light filters or wearing blue light-blocking glasses can help improve sleep quality.
Caffeine and Alcohol Intake
Caffeine and alcohol can have a significant impact on sleep. Caffeine is a stimulant that can interfere with falling asleep and staying asleep, especially if consumed close to bedtime. Alcohol, while initially inducing drowsiness, can disrupt the sleep cycle and lead to fragmented sleep. It is advisable to limit caffeine and alcohol intake, particularly in the evening hours, to promote better sleep.
This image is property of www.sleepfoundation.org.
Medical Conditions Linked with Insomnia
Insomnia can be associated with various medical conditions. Understanding these links can help individuals address underlying issues and seek appropriate treatment.
Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep. It can cause fragmented sleep and lead to insomnia symptoms. Treating sleep apnea through methods such as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy can help alleviate insomnia.
Restless Leg Syndrome
Restless leg syndrome is a neurological condition characterized by uncomfortable sensations in the legs, often accompanied by an urge to move them. These sensations can disrupt sleep and contribute to insomnia. Treating restless leg syndrome through medication and lifestyle adjustments can improve sleep quality.
Mental Health Disorders
Many mental health disorders, such as anxiety and depression, can coexist with insomnia. These conditions can interact with and exacerbate insomnia symptoms. Managing mental health through therapy, medication, and other interventions can help address insomnia as well.
Chronic Pain
Chronic pain conditions, such as fibromyalgia or arthritis, can disrupt sleep patterns and contribute to insomnia. Managing chronic pain through pain management strategies and appropriate medical interventions can improve sleep quality.
Diagnostic Processes for Insomnia
Diagnosing insomnia involves a comprehensive evaluation of sleep patterns and potential underlying causes. Various diagnostic processes are used to assess and identify insomnia.
Physical Exams
Physical exams may be conducted to rule out any underlying medical conditions that could be contributing to insomnia. This may include assessing vital signs, conducting blood tests, and evaluating overall physical health.
Sleep History Analysis
A detailed sleep history analysis involves documenting sleep patterns, habits, and potential triggers for insomnia. It may include keeping a sleep diary, which can help identify patterns and factors contributing to sleep disturbances.
Sleep Studies and Their Importance
Sleep studies, such as polysomnography, can be conducted to monitor sleep patterns and identify any underlying sleep disorders. These studies involve monitoring brain activity, eye movements, heart rate, and breathing during sleep. Sleep studies are an important tool in diagnosing and treating insomnia.
This image is property of www.sleepfoundation.org.
Treatment Options for Insomnia
There are various treatment options available for managing and treating insomnia. These options can be tailored to the individual’s specific needs and may involve a combination of approaches.
Pharmacological Treatments
Pharmacological treatments, such as sleeping pills or sedatives, may be prescribed for short-term use to alleviate insomnia symptoms. It is important to use these medications under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as they can have side effects and the potential for dependency.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I)
CBT-I is a highly effective, evidence-based approach for treating insomnia. It involves identifying and addressing negative sleep patterns and thoughts through techniques such as sleep restriction, stimulus control, and relaxation training. CBT-I aims to retrain the brain and establish healthy sleep habits.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
In addition to addressing underlying causes and utilizing behavioral techniques, lifestyle and home remedies can also improve sleep quality. These may include establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a sleep-friendly environment, practicing relaxation techniques, and incorporating lifestyle adjustments such as exercise and proper nutrition.
Alternative Medicine Approaches
Some individuals may explore alternative medicine approaches to manage insomnia. These can include practices such as acupuncture, herbal remedies, and aromatherapy. While the effectiveness of these approaches may vary, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any alternative treatments.
Improving Sleep Hygiene for Better Rest
Improving sleep hygiene is essential for achieving better rest and managing insomnia. Adopting healthy sleep habits can significantly impact sleep quality and overall well-being.
Establishing a Regular Sleep Schedule
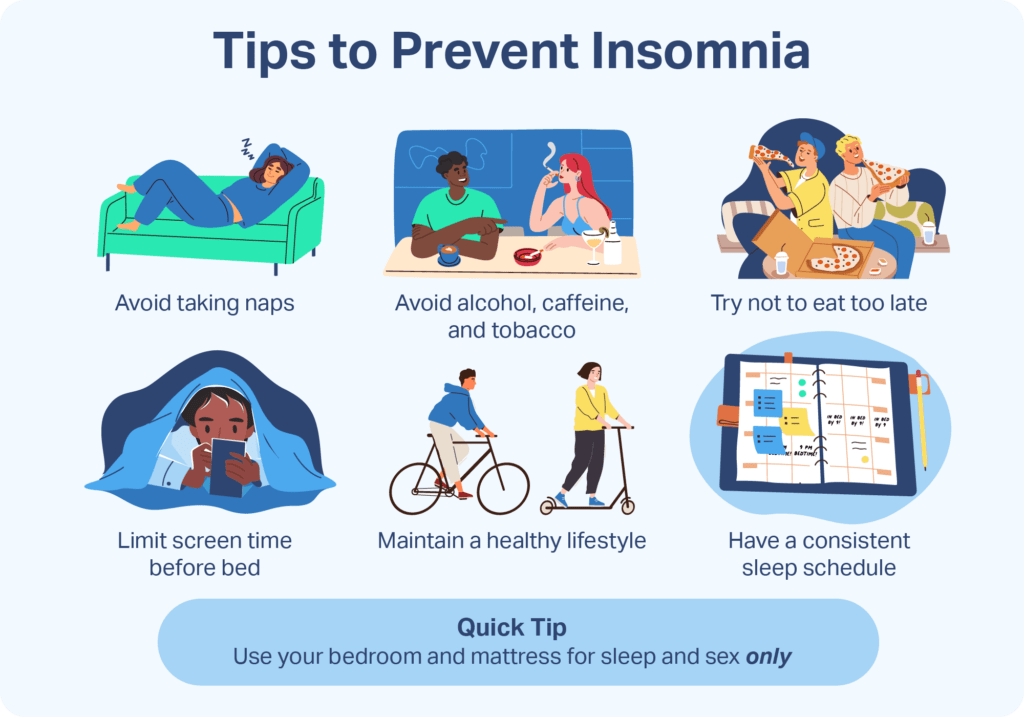
Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule can help regulate the body’s internal clock and improve sleep quality. Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, even on weekends, can train the body to fall asleep and wake up more easily.
Creating a Restful Environment
A restful sleep environment is conducive to quality sleep. This includes ensuring a comfortable mattress and pillow, controlling noise levels, maintaining a cool temperature, and creating a dark and quiet bedroom environment.
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Incorporating mindfulness and relaxation techniques into a bedtime routine can promote relaxation and prepare the body for sleep. This can include practices such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery.
Limiting Naps and Adjusting Diet
Limiting daytime napping and avoiding heavy meals close to bedtime can improve sleep quality. Napping for prolonged periods or consuming heavy meals can disrupt the sleep-wake cycle and make it harder to fall asleep at night.
This image is property of sleepopolis.com.
Technology and Insomnia
Technology has become an integral part of our lives, but it can also impact sleep quality. Understanding the effects of technology on sleep and implementing appropriate measures is essential for managing insomnia.
Apps for Better Sleep
There are several apps available that can help individuals monitor and improve their sleep quality. These apps may track sleep patterns, provide relaxation techniques, and offer guided meditations or white noise to promote better sleep.
Wearable Sleep Trackers
Wearable sleep trackers can provide valuable insights into sleep patterns, such as duration and quality of sleep, awakenings, and sleep stages. These devices can help individuals identify potential triggers for insomnia and make necessary adjustments to improve sleep quality.
The Impact of Screens on Sleep Quality
The blue light emitted by screens, such as smartphones, tablets, and computers, can suppress the production of melatonin and disrupt sleep. Limiting screen time, especially before bed, and utilizing features such as night mode or blue light filters can minimize the impact on sleep quality.
Digital Detox for Improved Sleep
Taking regular breaks from technology, such as implementing a digital detox before bed, can help promote better sleep. Engaging in relaxing activities, such as reading a book or practicing a hobby, instead of screen time can support a healthy sleep routine.
Preventing Insomnia
Preventing insomnia involves adopting healthy habits and managing potential triggers. Implementing strategies for stress management, engaging in physical activity, making dietary adjustments, and maintaining a healthy sleep environment are key.
Strategies for Stress Management
Practicing stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, deep breathing exercises, and engaging in hobbies or activities that promote relaxation, can help prevent the development of insomnia. It is important to find healthy coping mechanisms for managing stress.
Importance of Physical Activity
Regular physical activity has been shown to improve sleep quality. Engaging in activities such as walking, jogging, yoga, or other forms of exercise can promote better sleep. It is advisable to avoid intense exercise too close to bedtime, as it may stimulate the body and disrupt sleep.
Dietary Adjustments for Better Sleep
Avoiding heavy meals, especially close to bedtime, can help prevent digestive discomfort and promote better sleep. It is also important to limit caffeine and alcohol intake, as these substances can interfere with sleep patterns.
Maintaining a Healthy Sleep Environment
Creating a sleep-friendly environment is crucial for preventing insomnia. This includes keeping the bedroom cool, dark, and quiet, as well as ensuring a comfortable mattress and pillow. Removing electronic devices from the bedroom can also minimize distractions and promote better sleep.
In conclusion, understanding the risks and solutions associated with insomnia is essential for managing this common sleep disorder. By recognizing the signs, addressing underlying causes, and implementing healthy lifestyle habits, individuals can improve their sleep quality and overall well-being. Seeking professional help and exploring various treatment options can provide the support needed to overcome insomnia and achieve restful nights of sleep. Remember, prioritizing your sleep health is an investment in your overall health and happiness.
This image is property of www.sleepfoundation.org.