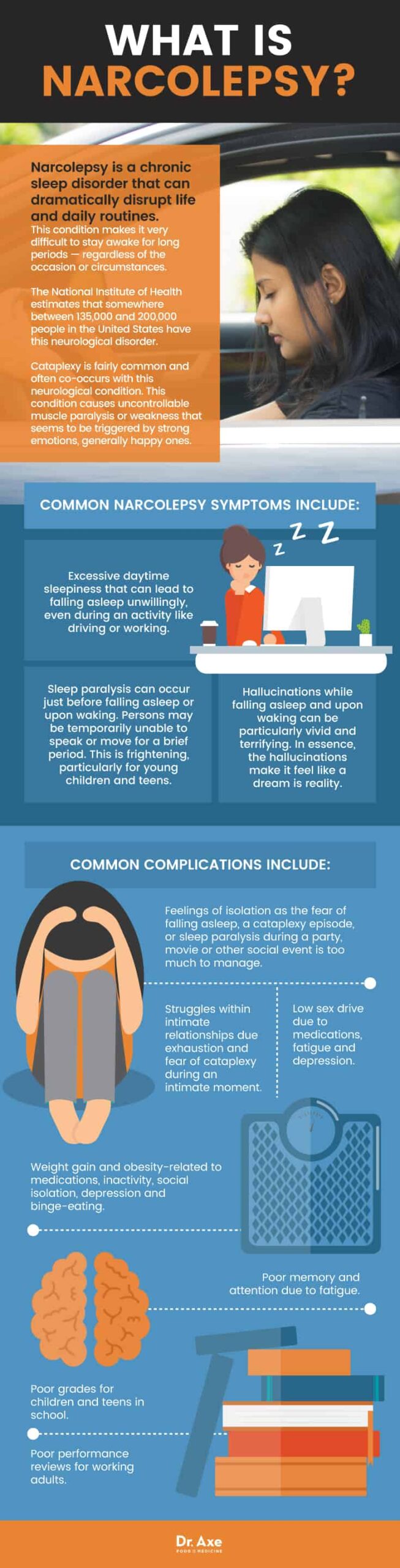
How Much Sleep Do You Need By Age?

Embarking on a journey to better understand your sleep needs is a pivotal step toward enhancing your overall health and well-being. “How Much Sleep Do You Need By Age?” illuminates the crucial, yet often overlooked, aspect of our lives: sleep. With insights from the reputable Vector Sleep Clinic, this article sheds light on the significance of addressing sleep disorders such as insomnia and sleep apnea, which can lead to severe health complications if left untreated. It emphasizes the importance of recognizing how sleep requirements change with age, providing a detailed guide to help you align your sleep habits with your body’s needs for optimal health, productivity, and quality of life. Whether you’re curious about the power of restful nights or seeking solutions for uninterrupted sleep, understanding your unique sleep needs is a critical step towards unlocking the magic of rejuvenating rest.
This image is property of pixabay.com.
Understanding Sleep Needs
Sleep is a fundamental component of your health and well-being, impacting everything from your physical health to your mood and cognitive abilities. It’s not just about getting enough hours; it’s about understanding the quality and structure of your sleep to ensure you’re truly rested.
The importance of sleep for health and well-being
Adequate sleep is as crucial to your health as a balanced diet and regular exercise. It helps to repair your body, consolidate memories, and regulate emotions. A chronic lack of sleep can lead to serious health issues, including obesity, heart disease, high blood pressure, and diabetes.
Factors influencing sleep requirements
Your age, lifestyle, and overall health play significant roles in determining how much sleep you need. While genetics can influence your sleep patterns, factors such as stress levels, physical activity, and screen time before bed can significantly impact the quality of your sleep.
Overview of sleep cycles and stages
Sleep is composed of several cycles, each including stages of light, deep, and REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep. Each stage plays a critical role in brain function and physical health, making it important to complete multiple cycles for a restorative sleep experience.
Newborns (0-3 months)
During the first few months of life, newborns require a lot of sleep, but not all at once, mirroring a pattern that will evolve as they grow.
Understanding newborn sleep patterns
Newborns sleep in short bursts throughout the day and night, totaling about 14 to 17 hours. This irregular schedule aligns with their need for frequent feedings.
Appropriate sleep duration and naps
Ideally, newborns will get the sleep they need over the course of four to six naps throughout the day and night.
Tips for establishing good sleep habits
Creating a calm bedtime routine, even at this early stage, can help signal to your newborn that it’s time to sleep. Ensuring they’re comfortable and their environment is conducive to sleep will also support better sleep habits.
Infants (4-11 months)
As babies grow, their sleep needs and patterns begin to take on a more predictable structure.
Transitioning to solid sleep schedules
During this phase, most infants start sleeping longer at night and taking three to four naps during the day.
Average sleep needs and nap times
Infants generally need between 12 and 15 hours of sleep a day, gradually consolidating more of that sleep at night.
Coping with common sleep challenges
Sleep regression and teething can disrupt sleep patterns. Sticking to a bedtime routine and adjusting nap times can help manage these challenges.
Toddlers (1-2 years)
With increased physical and cognitive development, toddlers require less sleep but still benefit significantly from naps.
Importance of naps for toddlers
One to two naps during the day help toddlers recharge, aiding in their development and mood regulation.
Nighttime sleep duration
Toddlers need approximately 11 to 14 hours of sleep, including naps, with most of this time occurring at night.
Managing bedtime resistance
Establishing a consistent bedtime routine and sleep-friendly environment can minimize resistance and ensure your toddler gets the sleep they need.
This image is property of pixabay.com.
Preschoolers (3-5 years)
As children enter preschool, their world expands, and so do the influences on their sleep.
Adjusting from naps to full night sleep
Many preschoolers drop their last nap during this stage, making a full night’s sleep even more critical for their health and development.
Typical sleep duration and quality
Preschoolers need about 10 to 13 hours of sleep per night. Ensuring a consistent bedtime helps promote sleep quality.
Dealing with nightmares or sleep disturbances
Maintaining a calm, secure bedtime environment and routine can help reduce the frequency of nightmares and night wakings.
School-age Children (6-13 years)
School-aged children’s sleep is vital for their growth, learning, and emotional regulation.
The role of sleep in growth and learning
Adequate sleep supports cognitive development, attention, and academic performance, as well as physical growth.
Recommended sleep hours
Children in this age group should aim for 9 to 11 hours of sleep each night.
Encouraging consistent sleep schedules
A consistent sleep schedule and bedtime routine remain important, as do limits on screen time in the evening to ensure quality sleep.
This image is property of pixabay.com.
Teenagers (14-17 years)
The teenage years bring significant changes that affect sleep needs and patterns.
Balancing sleep with school and social life
Teens often face challenges balancing schoolwork, extracurricular activities, and social time, leading to reduced sleep.
Effects of puberty on sleep
Puberty shifts the internal clock, making it natural for teens to fall asleep later. However, early school start times don’t align with this shift, often resulting in sleep deprivation.
Strategies for healthier sleep habits
Encouraging good sleep hygiene, including regular sleep schedules and reducing screen time before bed, can help teens get the sleep they need.
Young Adults (18-25 years)
This life stage includes new freedoms and responsibilities, which can impact sleep patterns and overall health.
Navigating sleep challenges in young adulthood
Balancing work, school, and social demands can lead to inconsistent sleep schedules and decreased sleep quality.
Ideal sleep duration for optimal performance
Young adults should aim for 7 to 9 hours of sleep per night for optimal health, mood, and productivity.
Impact of lifestyle choices on sleep
Alcohol, caffeine intake, and irregular schedules can significantly affect sleep quality. Making mindful lifestyle choices can support better sleep.
Adults (26-64 years)
During adulthood, the challenges of work, family, and health can impact sleep quantity and quality.
Maintaining sleep priority among work and family
Balancing these demands while making sleep a priority is crucial for long-term health and well-being.
Standard sleep requirements
Adults need 7 to 9 hours of sleep per night, though individual needs can vary.
Managing stress for better sleep
Developing strategies for stress management, such as exercise, relaxation techniques, and maintaining a work-life balance, can positively affect sleep.
Improving Sleep Health: Practical Tips
Creating a restful sleep environment
Ensure your bedroom is quiet, dark, and at a comfortable temperature. Investing in a good quality mattress and pillows can also enhance sleep quality.
The role of diet and exercise in sleep quality
A balanced diet and regular physical activity can significantly improve sleep. However, avoid heavy meals, caffeine, and intense exercise close to bedtime.
Mindfulness and relaxation techniques for better sleep
Practices such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can help prepare your mind and body for rest, promoting a more restful night’s sleep.