Causes of Restless Legs Syndrome
Imagine waking up in the middle of the night, unable to find comfort as an irresistible urge to move your legs overwhelms you. This is just one of the many symptoms of Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS). At Vector Sleep Clinic, we understand the impact that sleep disorders can have on your health and well-being. With our licensed and insured facility conveniently located in the heart of Rego Park, we offer comprehensive care to help you unlock the magic of restful nights, where dreams meet rejuvenation. In this article, we will explore the causes of Restless Legs Syndrome, shedding light on what may be keeping you up at night. So, why should you consider completing a sleep study? Let’s find out.
Definition and Overview of Restless Legs Syndrome
Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS) is a neurological disorder characterized by an irresistible urge to move the legs, often accompanied by uncomfortable sensations in the legs. This condition typically worsens during periods of inactivity and can significantly disrupt sleep and daily activities. While the exact cause of RLS is still unknown, various factors, including genetic, neurological, lifestyle, and medical conditions, play a role in its development and severity.
Understanding Restless Legs Syndrome
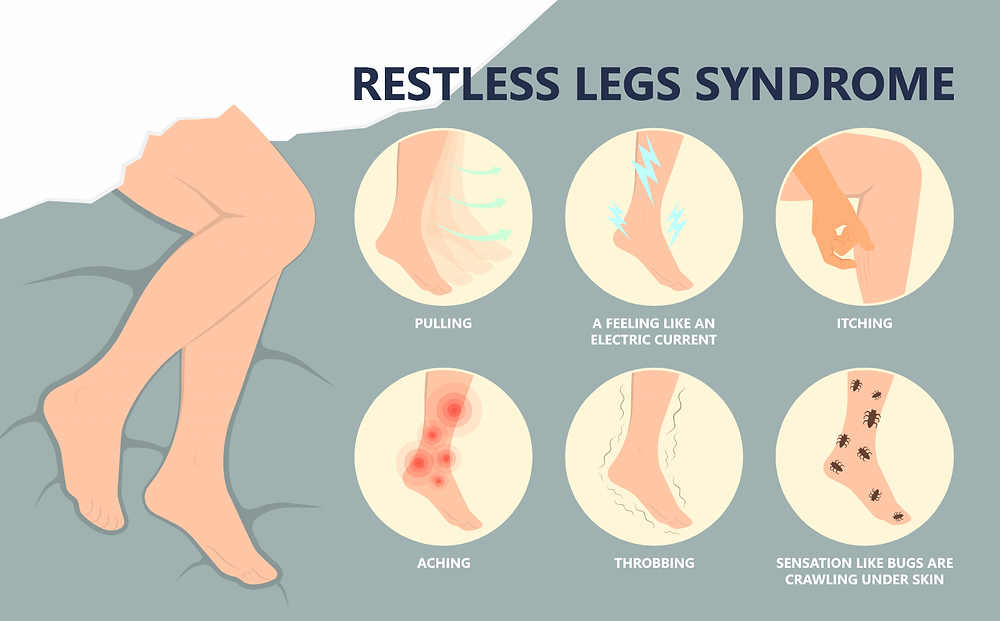
Restless Legs Syndrome is a condition that affects both men and women of all ages, although it tends to be more common in middle-aged and older individuals. The symptoms of RLS can vary from mild to severe and may include sensations such as tingling, crawling, itching, or aching in the legs. These sensations are usually relieved by movement, such as walking or stretching.
Symptoms and Diagnosis Criteria
To be diagnosed with Restless Legs Syndrome, you must meet certain criteria set by medical professionals. These criteria include having an urge to move your legs accompanied by uncomfortable sensations, worsened symptoms during periods of rest or inactivity, relief from movement, and symptoms that worsen or occur primarily in the evening or at night. RLS can often be misdiagnosed or overlooked, so it is essential to seek medical evaluation if you experience these symptoms.
Epidemiology of Restless Legs Syndrome
The prevalence of Restless Legs Syndrome varies among different populations and countries. Studies have shown that approximately 3-15% of adults worldwide have RLS. It is more prevalent in older adults and tends to affect women more than men. Additionally, individuals with certain chronic conditions, such as end-stage renal disease and iron deficiency anemia, are more likely to develop RLS.
Genetic Factors
The Role of Heredity in Restless Legs Syndrome
There is evidence to suggest that Restless Legs Syndrome may have a hereditary component. Research has found that approximately 40-60% of individuals with RLS have a family history of the condition. Having a close relative with RLS increases the likelihood of developing the disorder. However, genetic factors alone do not fully explain the development of RLS, and other factors play a significant role as well.
Identified Genetic Markers
Several genetic markers associated with RLS have been identified through research. One of the significant genetic variations linked to RLS is a mutation in the MEIS1 gene. This mutation is believed to affect the development and function of the central nervous system and plays a role in regulating dopamine, a neurotransmitter involved in movement control.
Family History and Risk Factor Assessment
If you have a family history of Restless Legs Syndrome, particularly among your parents or siblings, you may be at a higher risk of developing the condition. It is essential to inform your healthcare provider about your family history so that they can consider this factor when evaluating your symptoms and determining the appropriate course of treatment.
Neurological Factors
Dopamine Dysfunction and Its Implications
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter involved in controlling movement and is believed to be a key player in Restless Legs Syndrome. Research suggests that individuals with RLS may have altered dopamine activity in the brain, leading to the characteristic symptoms of the condition. Medications that increase dopamine levels, such as certain Parkinson’s disease drugs, often provide relief for individuals with RLS.
Brain Iron Deficiency
Iron is essential for the production of dopamine in the brain. Some studies have found a link between low brain iron levels and Restless Legs Syndrome. Iron deficiency in the brain may disrupt the normal functioning of dopamine and contribute to the development or worsening of RLS symptoms. Further research is needed to fully understand the relationship between iron deficiency and RLS.
The Impact of Nervous System Disorders on RLS
Certain neurological disorders, such as peripheral neuropathy and multiple sclerosis, have been associated with an increased risk of developing Restless Legs Syndrome. These conditions affect the peripheral nerves or the central nervous system, respectively, and may disrupt the normal functioning of the nervous system, leading to the onset or worsening of RLS symptoms.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Influence of Lifestyle Choices on RLS Symptoms
Certain lifestyle choices can affect the severity of Restless Legs Syndrome symptoms. For example, excessive consumption of caffeine, alcohol, and tobacco has been found to worsen RLS symptoms. Likewise, engaging in a sedentary lifestyle and prolonged periods of sitting or inactivity can increase the discomfort experienced by individuals with RLS.
The Role of Diet and Nutrition
Maintaining a healthy diet and adequate nutrition is essential for managing Restless Legs Syndrome. Some studies suggest that deficiencies in certain vitamins and minerals, such as iron, folate, and magnesium, may contribute to the development or worsening of RLS symptoms. Incorporating a well-balanced diet that includes these essential nutrients may help alleviate RLS symptoms.
Impact of Sedentary Life and Exercise
Regular exercise has been found to be beneficial for individuals with Restless Legs Syndrome. Engaging in physical activity, such as walking or swimming, helps improve circulation, reduce discomfort, and promote better sleep. On the other hand, leading a sedentary lifestyle with minimal movement or exercise can aggravate RLS symptoms. Finding a balance between rest and activity is key to managing RLS effectively.
Medical Conditions and RLS
Chronic Diseases Linked with Restless Legs Syndrome
Several chronic diseases and medical conditions have been associated with an increased risk of developing Restless Legs Syndrome. These include end-stage renal disease, diabetes, Parkinson’s disease, and peripheral neuropathy. Managing the underlying medical condition is essential in addressing RLS symptoms and improving overall quality of life.
Pregnancy-Related Restless Legs Syndrome
Pregnancy is a time when hormonal and physiological changes can trigger or worsen Restless Legs Syndrome symptoms. Many pregnant women experience RLS, particularly in the third trimester. Hormonal fluctuations, iron deficiency, and increased blood volume during pregnancy are thought to contribute to the development of RLS in pregnant women. Treatment options during pregnancy may be limited, and it is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider for appropriate management.
Medications That May Exacerbate RLS Symptoms
Certain medications have been shown to worsen Restless Legs Syndrome symptoms. These include some antidepressants, antipsychotics, and antihistamines. If you have RLS and are prescribed any of these medications, it is important to discuss with your healthcare provider the potential impact on your symptoms and explore alternative treatment options if necessary.
Iron Deficiency
The Connection Between Iron Levels and RLS
Iron deficiency is associated with an increased risk of developing and exacerbating Restless Legs Syndrome. Iron plays a crucial role in dopamine production, and low levels of iron in the brain can disrupt the dopamine system, leading to RLS symptoms. Maintaining healthy iron levels through diet or iron supplementation may help alleviate symptoms and improve sleep in individuals with RLS.
Testing and Treatment for Iron Deficiency
If iron deficiency is suspected as a contributing factor to Restless Legs Syndrome, a blood test can be performed to measure iron levels in the body. Supplementing with iron may be recommended if low iron levels are detected. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any iron supplements, as excessive iron intake can also have adverse effects.
Effectiveness of Iron Supplementation
Research has shown that iron supplementation can be effective in improving Restless Legs Syndrome symptoms in individuals with low iron levels. However, it may take several weeks or months for the benefits to be fully realized. It is essential to closely monitor iron levels and work with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage and duration of supplementation.
Kidney Failure and Dialysis
Prevalence of RLS in Patients with Renal Failure
Restless Legs Syndrome is more prevalent in individuals with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) compared to the general population. Approximately 20-50% of patients receiving dialysis treatment for ESRD experience RLS symptoms. The exact mechanisms behind the association between kidney failure and RLS are not fully understood, but factors such as iron deficiency, uremia, and alterations in neurotransmitter function may play a role.
How Dialysis Impacts Restless Legs Syndrome
Dialysis, a treatment method for individuals with kidney failure, can have both positive and negative effects on Restless Legs Syndrome symptoms. On one hand, dialysis can help alleviate RLS symptoms by removing toxins and excess fluids from the body. However, the rapid changes in fluid and electrolyte balance during dialysis can also trigger or worsen RLS symptoms. Close monitoring and appropriate management are crucial for individuals with kidney failure and RLS.
Management of RLS in Kidney Disease
Managing Restless Legs Syndrome in individuals with kidney disease involves a comprehensive approach that addresses both the underlying renal condition and RLS symptoms. Treatment options may include iron supplementation, medications that target neurotransmitters such as dopamine, and lifestyle modifications, such as regular exercise and optimizing sleep hygiene. It is important for individuals with kidney disease and RLS to work closely with their healthcare team to develop an individualized treatment plan.
Sleep Deprivation and Disturbance
Interaction Between Sleep Quality and RLS
Restless Legs Syndrome can significantly disrupt sleep quality, leading to sleep deprivation and disturbance. The discomfort and urge to move the legs experienced by individuals with RLS often worsen during periods of rest or inactivity, particularly at night. Insufficient sleep due to RLS can further exacerbate symptoms and negatively impact overall well-being.
Effects of Sleep Loss on RLS Severity
Lack of adequate sleep can contribute to the severity of Restless Legs Syndrome symptoms. Sleep deprivation can lead to increased sensitivity to discomfort, intensified urges to move the legs, and heightened agitation. The resulting sleep disturbance can create a vicious cycle, with RLS symptoms causing sleep disruption and sleep disruption worsening RLS symptoms.
Managing Sleep Hygiene to Alleviate Symptoms
Adopting good sleep hygiene practices can help alleviate Restless Legs Syndrome symptoms and improve overall sleep quality. This includes maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a comfortable and conducive sleep environment, avoiding stimulating activities before bedtime, and practicing relaxation techniques. By prioritizing sleep hygiene, individuals with RLS can optimize their sleep and minimize the impact of symptoms on their daily lives.
Polysubstance Use
Impact of Caffeine, Alcohol, and Tobacco
Caffeine, alcohol, and tobacco use have been found to exacerbate Restless Legs Syndrome symptoms. Caffeine, commonly found in coffee, tea, and energy drinks, can disrupt sleep and increase agitation, worsening RLS symptoms. Alcohol, although it may initially provide a sedative effect, can disrupt sleep cycles and lead to increased restlessness. Smoking tobacco has also been associated with increased RLS severity, likely due to its stimulating effects.
Withdrawal and Its Effects on RLS
Withdrawal from substances such as caffeine, alcohol, and tobacco can initially worsen Restless Legs Syndrome symptoms. As the body adjusts to the absence of these substances, individuals may experience increased restlessness, discomfort, and difficulty sleeping. However, over time, withdrawal from these substances can lead to improved RLS symptoms, highlighting the importance of minimizing or eliminating their use.
Substance Use Disorder and Restless Legs
Substance use disorder, characterized by a dependence on and inability to control substance use, can have a significant impact on Restless Legs Syndrome. Individuals with substance use disorder may be more likely to develop RLS, and those with pre-existing RLS may experience worsened symptoms due to substance abuse. Proper treatment for substance use disorder, including addressing RLS symptoms, is crucial for overall well-being and recovery.
Current Research and Future Directions
Emerging Theories on Causes of Restless Legs Syndrome
While much progress has been made in understanding the different factors involved in Restless Legs Syndrome, there is still much to learn about its precise causes. Current research is exploring various avenues, including the role of immune system dysfunction, inflammation, and circadian rhythm disruptions. Scientists are also investigating the potential genetic and environmental interactions that contribute to the development and progression of RLS.
Ongoing Clinical Trials and Their Preliminary Findings
Numerous clinical trials are underway to further investigate Restless Legs Syndrome and develop more effective treatment options. These studies aim to evaluate the safety and efficacy of different medications, including those targeting dopamine and iron regulation. Preliminary findings from some ongoing trials suggest promising results, indicating potential advancements in managing RLS in the future.
Potential for New Treatments Based on Recent Discoveries
Recent discoveries in the field of RLS research have paved the way for potential new treatment approaches. For example, medications targeting novel neurotransmitter receptors and iron regulation mechanisms are being explored. Additionally, advancements in non-pharmacological interventions, such as transcranial magnetic stimulation, show promise in alleviating RLS symptoms. These exciting developments offer hope for individuals living with Restless Legs Syndrome and highlight the importance of continued research in this field.
In conclusion, Restless Legs Syndrome is a complex neurological disorder that involves various genetic, neurological, lifestyle, and medical factors. Understanding the different causes and contributing factors is crucial for effective management and treatment of RLS. By addressing these factors and working closely with healthcare professionals, individuals with Restless Legs Syndrome can find relief and improve their quality of life. With ongoing research and advancements in the field, there is hope for better treatments and improved outcomes for those living with RLS.